|
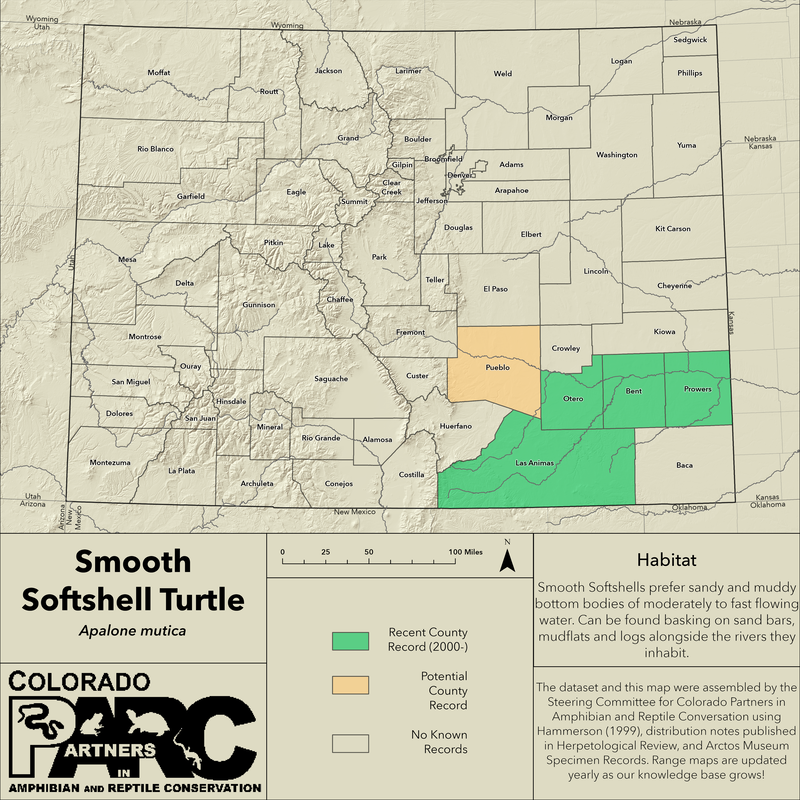
Distribution: In Colorado, they have been found in the Arkansas and Purgatory River, at elevations below 4,500ft (1372m). This species was first documented in the state of Colorado in Otero County during the 2018 COPARC Southeast Colorado Herpetofauna Inventory (Johnson et. al 2019), but has since had it's distribution expanded to Bent (Maloney 2020), Prowers (Johnson & McMullen 2021), and Las Animas (Warfel 2022) counties.
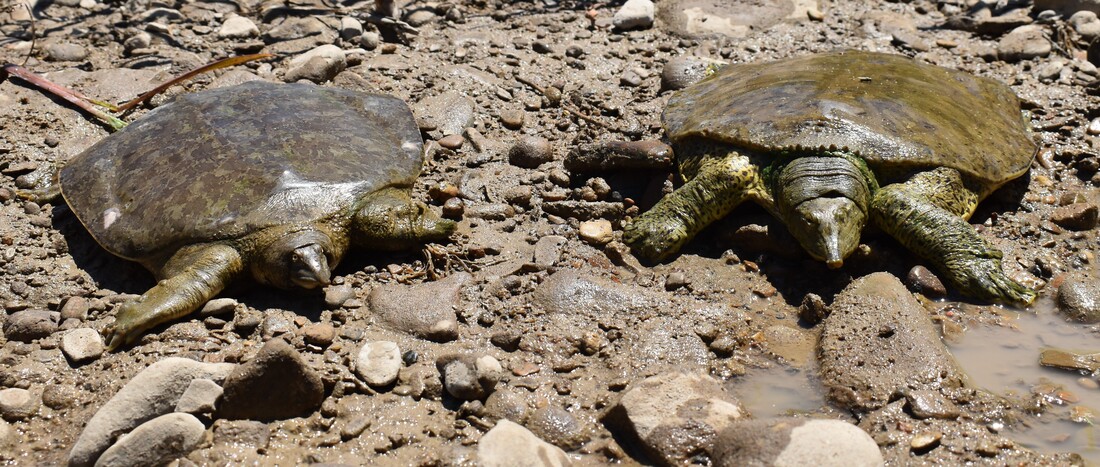
Activity: Being a diurnal species, Smooth Softshells are typically active between the months of March and October, with Colorado observations ranging from May to September. A very skittish species, they typically run away from any disturbance they encounter. They spend the majority of their active time basking or foraging for food, and when inactive, will bury themselves in the mud or sand at the bottom of the body of water they inhabit. (Collins 2010)
Conservation Status:
NatureServe rank: G5 (Globally Secure), S1 (State Critically Imperiled). CNHP Tracking Status: Watchlisted Only |
Habitat: Smooth Softshells prefer sandy and muddy bottom bodies of moderately to fast flowing water. Can be found basking on sand bars, mudflats and logs alongside the rivers they inhabit. (Collins 2010)
Diet: Smooth Softshells are opportunistic carnivores, known to eat a wide variety of invertebrates, from terrestrial and aquatic insects, to crayfish. They have also been observed to prey upon fish, amphibians, small birds and small mammals. (Collins 2010)
Defense: When threatened they will typically run into the water and swim with the flow of the river to escape predators, occasionally going the extra step of burying themselves into the bottom of the river to avoid detection or predation attempts. (Collins 2010)
Natural Predators: As eggs and juveniles, they are occasionally preyed upon by predatory birds, snakes, fish, bullfrogs, other turtles and small to medium sized mammals. As adults they have very few predators but likely are sensitive and susceptible to water pollution or other environmental disturbances. (Collins 2010)
|
Cited & Additional Resources
- Collins, J. T., Collins, S. L., Taggart, T. W., & Collins, J. T. (2010). Amphibians, reptiles and turtles in Kansas. Eagle Mountain Publishing.
- Johnson et al. 2019. Apalone mutica. Geographic Distribution: Colorado State Record & Otero County, Colorado County Record. Herpetological Review 50:522.
- Johnson & McMullen. 2021. Apalone mutica. Geographic Distribution: Prowers County, Colorado County Record. Herpetological Review 52:572.
- Collins, J. T., Collins, S. L., Taggart, T. W., & Collins, J. T. (2010). Amphibians, reptiles and turtles in Kansas. Eagle Mountain Publishing.
- Johnson et al. 2019. Apalone mutica. Geographic Distribution: Colorado State Record & Otero County, Colorado County Record. Herpetological Review 50:522.
- Johnson & McMullen. 2021. Apalone mutica. Geographic Distribution: Prowers County, Colorado County Record. Herpetological Review 52:572.
Account compiled by: Hunter Johnson & Rémi Pattyn
Reviewed by: Hayden Lewis
Last Updated: 2/10/2022 by Hunter Johnson
Reviewed by: Hayden Lewis
Last Updated: 2/10/2022 by Hunter Johnson